Report to/Rapport au :
Corporate
Services and Economic Development Committee
Comité des services organisationnels et du développement économique
and Council/et au Conseil
08 May 2008 / le 08 mai 2008
Submitted
by/Soumis par : Nancy Schepers,
Deputy City Manager/Directrice municipale adjointe,
Planning, Transit and the
Environment/Urbanisme, Transport en commun et Environnement
Contact Person/Personne ressource : Rob Mackay, A/Director
Economic
and Environmental Sustainability/Direction de la viabilité économique et de la
durabilité de l’environnement
(613)
580-2424 x 22632, rob.mackay@ottawa.ca
|
|
Ref N°: ACS2008-PTE-ECO-0015
|
SUBJECT:
|
BUILDING Ottawa's
eCONOMIC PROSPERITY - a funding request to support ocri initatives
|
|
|
|
OBJET :
|
Favoriser
la prospérité économique d'Ottawa – demande
de financement pour soutenir les initiatives du OCRI
|
REPORT
RECOMMENDATION
That the Corporate Services and Economic Development
Committee recommend Council approve up to $520,000 in
partnership funding to the Ottawa Centre for Research
and Innovation (OCRI) to support the delivery of to
the following programs:
·
Regional
Innovation Network (RIN);
·
Ontario
Research Commercialization Project (ORCP);
·
Investment
Attraction; and
·
Cluster
Support.
RECOMMANDATION DU RAPPORT
Que le Comité des
services organisationnels et du développement économique recommande au Conseil
d’approuver un cofinancement d’une valeur de 520 000 $ avec le Centre
de recherche et d’innovation d’Ottawa (OCRI) en vue de soutenir la prestation
des programmes suivants :
·
Réseaux
régionaux d’innovation (RRI);
·
Programme
ontarien de commercialisation de la recherche (POCR);
·
Attraction
des investissements; et
·
Soutien
aux grappes.
BACKGROUND
The Ottawa
Centre for Research and Innovation (OCRI) is a non-profit agency supported by
over 650 private sector members along with federal, provincial and municipal
funding partners.
OCRI’s activities include the
delivery of:
·
Programs to support entrepreneurs from
pre-start-up to expansion through its Entrepreneurship Centre;
·
Investment attraction and facilitation
services through its Global Marketing arm; and
·
Commercialization of technology
programs through its Investment and Commercialization arm.
OCRI also
undertakes:
·
Delivery of business advisory
services;
·
Delivery of educational seminars;
·
Dissemination of business education
materials;
·
Hosting of networking events;
·
Participation in investment and trade
missions and prospecting abroad;
·
Conducting investment market research;
·
Facilitation of prospective investors
(including site selection, and business partner introductions);
·
Linking businesses with university,
government and private-sector research and researchers;
·
Linking businesses with capital
funding sources (including debt and investment); and
·
Promoting science and technology
education choices through programs to familiarize students with
high-tech-business career and entrepreneurial opportunities.
OCRI uses
funding from federal, provincial, municipal, member, and fee-for-service
sources to finance its activities. Many
of the federal and provincial funding programs that OCRI participates in
require municipal matching funds to demonstrate local support.
Regional
Innovation Network
(RIN) - Request
for $250,000 in
City partnership funding
In
order to access $260,847 from the Ontario Ministry of Research and
Innovation’s RIN
program in 2008,
OCRI is requesting $250,000 in partnership funding from
the City of Ottawa.
These funds will be supplemented with an additional $358,643 in the form of
private sector contributions allowing for a total project allocation of
$869,490.
This is
the last year of a three-year
provincial funding program which has contributed
$1,400,000 in support toward
the Regional Innovation Network. In both 2006 and 2007, the City
has contributed $250,000 to this program. This
year’s request will enable OCRI to meet the
growing demand for services from the Cleantech and Ottawa MedTech Networks. It
will also enable
the growth of a therapeutics network, create better linkages to the research
community, and enhance the capacity of the Investment and Commercialization
Group to
build and grow start up and emerging companies in Ottawa.
Ontario
Research Commercialization
Project (ORCP) - Request
for $100,000 in
City partnership funding
In
order to access $422,500 from
the ORCP in 2008, OCRI is requesting $100,000 in partnership
funding from the City of Ottawa. These funds will be
combined with private sector contributions of $322, 500 to create a project
fund totalling $845,000.
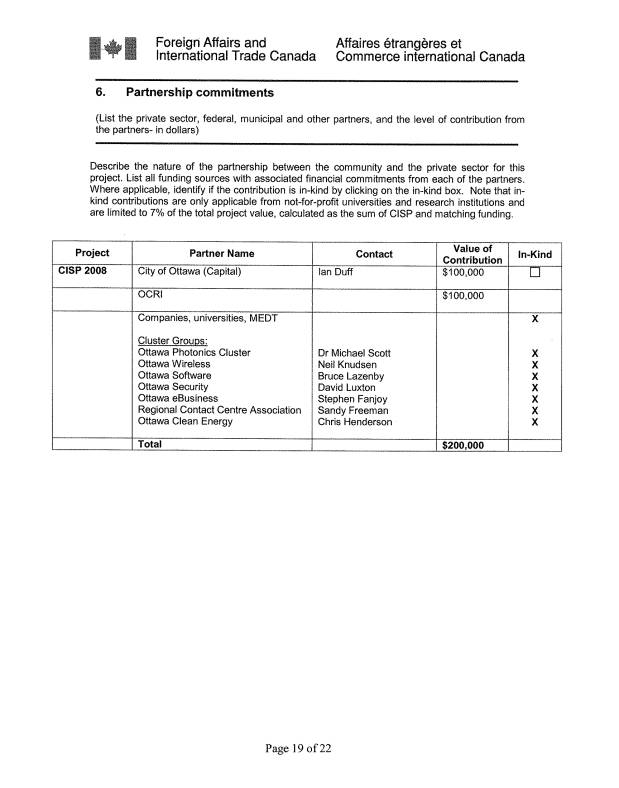
Investment
Attraction – Request for $100,000 in
City partnership funding
In order to
access $200,000 from the Department of Foreign Affairs and
International Trade’s (DFAIT) Community
Investment Support Program (CISP) in
2008, OCRI is
requesting $100,000 in
partnership funding from
the City and $100,000 from private sector and partner contributions. If successful, the
City’s $100,000 investment will allow OCRI to expand
its capacity for investment attraction activities by $400,000.
OCRI
continues to execute lead generation activity under DFAIT’s CISP program. Under
CISP, OCRI has focused
on establishing global networks, testing and understanding various geographic
markets, competitive forces and developing regional messaging. The 2008 lead
generation program will target gaming/new media, security, clean energy and
medical devices/convergent
technologies in priority US markets. It will promote Ottawa as a major
innovation hub in targeted global markets and continue to execute investment
attraction activity in India, China, and the United Kingdom. Based on continued
support from the City
and building on our past success, OCRI expects to
generate more than 80
international leads in 2008 under this program.
The
Canadian Department of Foreign Affairs and International Trade delivers
the Community Investment Support Program (CISP) which helps to
build local investment attraction capacity.
CISP requires matching funds from the municipality of the applicant
organization.
In order to access $200,000 from the CISP in 2008,
OCRI needs $100,000 from the City and $100,000 from private sector and partner
contributions. If successful, OCRI will thus be able to expand its
capacity for investment attraction activities by $400,000 through a $100,000
investment by the City.
Within
the Ottawa’s Economic Strategy, the City has been committed to a cluster-based
economic development policy. An industry cluster is a group of
companies that produce, mainly for export, similar products and/or services
within a close geographic proximity such as a municipality or region. In
response to the City’s approach to cluster-based economics, OCRI
developed and implemented a cluster support model that supports cluster growth
while minimizing the demand for new funds. The
City supported this pilot project with $140,000 over the past two years. The
result of this pilot project has been the creation of a logistic support system
that is now supporting eight
clusters through a set of productivity tools within the Global Marketing
section of OCRI. In 2008, the
clusters have defined a series of strategic initiatives that will strengthen
and help grow the Ottawa economy. This
current funding
request will support a High School Pilot Technology Centre Project (Software),
a Federal
Industrial Benefits Capture Initiative (Security, Wireless, Software and
Cleantech), an
Industry recognition campaign (Contact Centres), and a Joint Targeted Marketing
Initiative (Semiconductor).
High-tech cluster businesses in Ottawa have
collectively identified strategic initiatives that they support to strengthen
Ottawa’s competitive position in their respective industries.
The software cluster has identified the need for a
High School Technology Centre to enthuse students about high technology study at
an early stage by offering high school credit programs at a shared facility
where all Ottawa high school students can obtain high-calibre technology
education and training. Direct project
costs and in-kind support totals $120,000 for this project.
The security cluster has identified an opportunity
for expansion through a Federal Industrial Benefits Capture Initiative. The Canadian Department of National Defence
is currently sourcing major capital programs to foreign businesses due to
insufficient capacity in Canadian industry.
However, the foreign businesses are obligated to procure from Canadian
suppliers - whether for inputs to the projects or not. This initiative would build awareness
through focussed seminars, development of a database of programs, prime
contactors and their associated offset obligations, arrangement of meetings
between prime contractors, industry experts and Ottawa businesses, and through
linking Ottawa businesses with potential opportunities for business
development. Direct project costs and
in-kind support totals $150,000 for this project.
The contact centre cluster has identified the need
to improve public perception of the industry in Ottawa. Its proposed Contact Centre Industry
Recognition Campaign would inform the public, students (as potential
employees), and investors of the well-paying and excellent career opportunities
afforded by businesses in the Ottawa cluster.
Direct project costs and in-kind support totals $75,000 for this
project.
The semiconductor cluster has identified the need
to collaborate on a cooperative marketing and sales approach targeted to the
Taiwan market for wireless telecommunications.
Its Semiconductor Partnering Initiative would identify collaborators, prepare
a cooperative strategy and begin its implementation. Direct project costs and in-kind support totals $80,000 for this
project.
DISCUSSION
Ottawa’s 20/20
Economic Strategy was guided by the directive to develop and support strong
export-based economic generators. In
its guiding principle “An Innovative City Where Prosperity is Shared Among
All”, the Strategy identifies that the City should “accelerate the growth of
export industries to increase the wealth of Ottawa’s local and rural
economies”. The Strategy also
established the following policies:
- The City will support the ability of
Ottawa research institutions and industry clusters to turn research and
discoveries into products and services (number 15);
- The City will work with local
economic stakeholders to develop and promote marketing expertise to
improve product-to-market success (number 18);
- The City will work with its economic
agencies and TOP to manage collaboration and advance cluster development
(number 19);
- The City will support and strengthen
entrepreneurial capacity by promoting its value and improving access to
training and development (number 22);
- The City in collaboration with other
stakeholders in Ottawa’s economy will facilitate access to investment
capital and identify and promote alternate sources of capital for business
start-up and expansion (number 23); and
- The City will support OCRI’s Ottawa
Global Marketing and other stakeholders to promote Ottawa as a unique
centre for business, talent and investment (number 26).
The funding
requested in this report is to support those initiatives which
proposed in this report respond
directly to these policies and their intentions within the 20/20 Economic
Strategy.
Regional
Innovation
Network (RIN)
More specifically, the
Regional Innovation Network includes
a full-service investment and commercialization program for start-up and
emerging companies in the life science, cleantech, and Information and Communications
Technologies (ICT)
sectors including:
·
Access
to mentors;
·
Market
intelligence;
·
Business
advisory services; and
·
Access
to capital
This program
has also launched a business accelerator, an
expansion of Cleantech Initiative (formerly the
Bioproducts, Energy and Environmental Technologies Business Network), and a
launch of the Ottawa MedTech Network (formerly the
Ottawa Medical Devices Network).
By approval of the City’s funds,
and under the RIN program, the following deliverables will
be achieved:
·
Participation in Canada’s
Top 10 Investment forums in Boston, New York, San Francisco as well as call for
applications for 2008/09 and hosting Canada’s Top 10 investment bootcamp;
·
Facilitating
investment interest in six
Ottawa Life Science and Cleantech companies;
·
Business
advisory services to 60 new start-up or emerging companies;
·
Facilitating
mentorships for four Ottawa companies, in partnership with the National
Research Council’s Industrial Research Assistance Program;
·
Facilitating
access into the Ontario Business Mentorship and Entrepreneurship Program for two
new Ottawa companies;
·
Representing
Ottawa at the World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology and Bioprocessing;
·
Hosting
a Green Buildings showcase in Ottawa;
·
Hosting
a Clean Energy Forum in Ottawa;
·
Representing
Ottawa at Bio 2008 in San Diego, California;
·
Graduating
one company through the business accelerator and taking another into it;
·
Participation
in BioFinance 2008, BioNorth 2008, and Cleantech Research Showcase;
·
Organize
and host the Ottawa Life Sciences Achievement Awards; and
·
Facilitate
networking events for Ottawa MedTech.
Ontario
Research Commercialization
Program (ORCP)
Components of the ORCP program will
include:
·
Development
of market/competitive intelligence
including searches of electronic libraries and databases;
·
Establishment
of business opportunity networks
by using business development officers to search for technology
commercialization opportunities among their network of businesses, researchers,
and others in order to connect appropriate collaborators for commercial and
economic results;
·
Development
of entrepreneurial capabilities by
imparting essential skills for business success to
technically-oriented small-business proprietors, connecting the business
proprietors with seasoned mentors, other businesses, service providers,
researchers, and business opportunities.
Seminars, training courses, conferences, venture fairs, workshops and
networking events will also be delivered
to enhance the capabilities of Ottawa’s entrepreneurs; and
·
Exploration
of technology convergence is
being explored
through linking such sectors as Information and Communications Technology (ICT)
with Life Sciences for commercial opportunities (e.g. Bioinformatics). Other sectors being explored for convergence
include automotive, aerospace, energy, manufacturing, finance, etc
If
successful, OCRI through a $350,000 investment by the City to the RIN
and OCRP will be able to
expand its capacity for commercialization of innovation activities by $710,847.
Investment
Attraction
The investment
attraction activity proposed under this request for City funding participation
includes:
- Analysis of business intelligence
from the Ottawa Technology Industry Guide data and acquisition tracking
data;
- Execution of an outcall program to
identified businesses that pose a retention risk or expansion potential;
- Development of a strategy to
maximize benefits and minimize risks to the local economy of strategically
important companies in the Ottawa region;
- Refinement of the Ottawa value
proposition relating to outsourcing and R&D for U.S. business
investment targets;
- Upgrading on-line resources in
support of the Ottawa value proposition;
- Investment missions in California
(San Diego and Silicon Valley), Washington D.C., and the New York-Boston
corridor focussed on the gaming/new media, security, clean energy, and
medical devices/convergent technologies sectors;
- Refinement of the Ottawa value
proposition to early stage companies in the U.K.;
- Improvement of on-line resources to
include a U.K. dimension;
- Investment missions (3) in U.K.
focussed on the wireless, gaming, security, photonics, and medical
devices/health services sectors;
- Investment missions to China (3),
including Hong Kong and Taiwan, focussed on the
telecommunications/wireless, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID),
photonics, clean energy, medical devices, and gaming/new media sectors;
- Enhancement of Chinese language
materials, including on-line resources;
- Enhancement of the integration of
Ottawa’s Chinese community into investment activities;
- Development of case studies to
support investment targets;
- Development of an investment program
around the GITEX show in Dubai, UAE featuring the Information and
Communications Technology sector;
- Development of material to support
three specific investment pursuits out of India;
- Development of a program to host
potential investors from India;
- Development of a program to build
support within the Ottawa Indian community;
- Development of on-line resources in
support of investment from India; and
- Support of an ICT investment mission
to Sao Paulo, Brazil and Santiago, Chile.
The Regional Innovation Network (RIN) program
includes a full-service investment and commercialization program for start-up
and emerging companies in the life science, cleantech, and ICT sectors
including:
·Access to mentors;
·Market intelligence;
·Business advisory services; and
·Access to capital
It has also launched a business accelerator,
expansion of Cleantech Initiative (formerly the Bioproducts, Energy and
Environmental Technologies Business Network), and launch of the Ottawa MedTech
Network (formerly the Ottawa Medical Devices Network).
Under the RIN program, the following deliverables
would be enabled by approval of this funding request to the City:
·Canada’s Top 10 Investment forums in Boston, New
York, San Francisco as well as call for applications for 2008/09 and hosting
Canada’s Top 10 investment bootcamp;
·Facilitating investment interest in 6 Ottawa Life
Science and Cleantech companies;
·Business advisory services to 60 new start-up or
emerging companies;
·Facilitating mentorships for 4 Ottawa companies, in
partnership with the National Research Council’s Industrial Research Assistance
Program;
·Facilitating access into the Ontario Business
Mentorship and Entrepreneurship Program for 2 new Ottawa companies;
·Representing Ottawa at the World Congress on
Industrial Biotechnology and Bioprocessing;
·Hosting a Green Buildings showcase in Ottawa;
·Hosting a Clean Energy Forum in Ottawa;
·Representing Ottawa at Bio 2008 in San Diego,
California;
·Graduating one company through the business
accelerator and taking another into it;
·Participation in BioFinance 2008, BioNorth 2008,
and Cleantech Research Showcase;
·Organize and host the Ottawa Life Sciences
Achievement Awards; and
·Facilitate networking events for Ottawa MedTech.
Components of the ORCP program include development
of market/competitive intelligence, establishment of business opportunity
networks, development of entrepreneurial capabilities, and exploration of
technology convergence. The
market/competitive intelligence project includes ad hoc
searches of electronic libraries and databases. The business opportunity networks are business development
officers who search for technology commercialization opportunities among their
network of businesses, researchers, and others in order to connect appropriate
collaborators for commercial and economic results. Entrepreneur development includes imparting essential skills for
business success to technically-oriented small-business proprietors, connecting
the business proprietors with seasoned mentors, other businesses, service
providers, researchers, and business opportunities. Seminars, training courses, conferences, venture fairs, workshops
and networking events are delivered.
Technology convergence is explored through linking such sectors as
Information and Communications Technology (ICT) with Life Sciences for
commercial opportunities (e.g. Bioinformatics). Other sectors being explored for convergence include automotive,
aerospace, energy, manufacturing, finance, etc.Cluster
Support
CONSULTATION
The Ottawa
Partnership has been consulted and do support the recommendations contained in
this report.
FINANCIAL IMPLICATIONS
The funding for
this initiative is available within the Economic Development Division’s 2008
Capital Budget allocation
SUPPORTING DOCUMENTATION
Document 1 Schedules A – OCRI Global Marketing (Investment Attraction) -
$100,00 Capital Request
Document 2 Schedule B – OCRI (Regional Innovation
Network) - $250,000 Capital Request
Document 3 Schedule C – OCRI (Ontario Research Commercialization Project)
- $100,000 Capital Request
Document 4 Schedule D – OCRI Global Marketing (Cluster Support) - $70,000
Capital Request
DISPOSITION
Upon Council approval of the
recommendations contained in this report, Economic Development staff will
proceed to formalize a funding agreement with OCRI and monitor their
activities.
SCHEDULES A – OCRI GLOBAL MARKETING
(INVESTMENT
ATTRACTION) - $100,00 CAPITAL REQUEST
|
OCRI Global Marketing
(Investment Attraction) $100,000 Capital Request
|
|
General
Background Information:
- Over the
past several years, OCRI has successfully executed investment activity
under Foreign Affairs and International Trade’s Community Investment
Support Program (CISP). CISP is a program developed to stimulate
cooperation between municipal governments and the private sector. Its
objective is to enhance the capability and effectiveness of Canadian
communities to attract, retain, and expand foreign direct investment.
CISP is a cost-shared program, which supports up to 50% of eligible costs for projects that are
part of a comprehensive business plan. The program supports activities
ranging from improving the “investment readiness” of communities through
to larger projects designed to attract, retain and expand foreign direct
investment.
- The
program is designed to support the implementation of incremental initiatives by
communities; it does not support
operational funding, operating projects and staff.
- Under
past CISP activity, OGM has concentrated on establishing global
networks, testing various geographic markets, understanding our markets
and competition and developing our messaging. One of the key lessons
learned has been the fact that Business Development, Partnership
Activity and Investment go hand in hand. The CISP projects have
contributed significantly to our success. Specific success has included
the development of extensive networks in the United States, most notably
in Washington DC, the American Southwest and New York/Boston. We have
achieved a better understanding of the European market and a significant
increase in partnership activity in the United Kingdom. We have achieved
a continuing refinement of our messaging and the development of our
material in several languages.
- For the
period 1 Apr 08- 31 Dec 08 OGM has applied for $200,000. The
adjudication committee will announce its funding decision by the end of
March 2008. To achieve the necessary matching for all the federal funds
awarded, OGM requires a further
$100,000 of funding to be able to complete the CISP program for 2008. These funds need to be identified in
a timely manner, as all CISP activity must be completed by December 31,
2008.
- Our City
Capital funding request is crucial to this CISP program. Failure to secure adequate matching
funds will result in defaulting on our CISP program and the return of a
minimum of $80,000 of funding to Foreign Affairs. In addition, future funding will be
jeopardized.
It is important to note that the CISP program does
not allow for the utilization of salaried staff. Therefore project implementation requires the use of incremental
human resources that are not covered by the City’s annual operating grant.
|
|
OCRI 2008 Capital Budget Request Details
|
City Capital Request
|
Other Support
|
CISP Support
|
Total
Project
|
|
Consulting Fees
|
60,000
|
|
|
|
|
Direct project costs
|
40,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
$100,000
|
$100,000
|
$200,000
|
$400,000
|
2008 CISP Strategic
Objectives:
OGM has been
approved by CISP to launch a series of specific projects that build on our
developed global relationships, embody the research and experience gained over
the last several years and position the Ottawa region to take advantage of
specific market opportunities.
Our activity for
2008 has a total budget of $400,000 and will focus on the following areas:
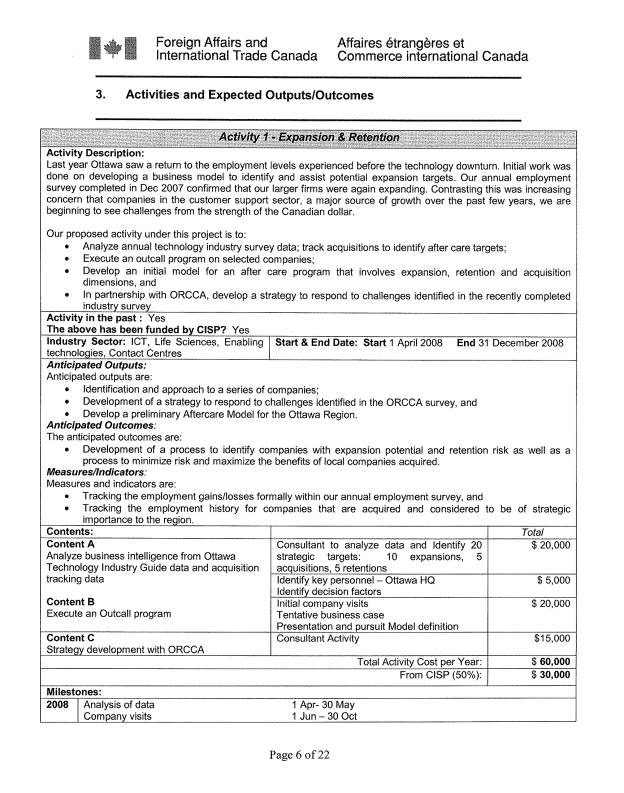
Expansion and Retention
Last year, Ottawa
saw a return to the employment levels experienced before the technology
downturn. Initial work was done on developing a business model to identify and
assist potential expansion targets. Our annual employment survey completed in
Dec 2007 confirmed that our larger firms were again expanding. Contrasting this
was increasing concern in many sectors, that the continued strength of the
Canadian dollar and the weakening of the US economy would create challenges to
continued growth.
Our proposed
activity under this project is to:
- Analyze annual technology industry
survey acquisition tracking data to identify after care targets;
- Execute an outcall program on selected
companies;
- Develop an initial model for an after
care program that involves expansion, retention and acquisition
dimensions, and
- In partnership with ORCCA (Ottawa
Region Contact Centre Association), develop a strategy to respond to
challenges identified in the recently completed industry survey of the
sector.
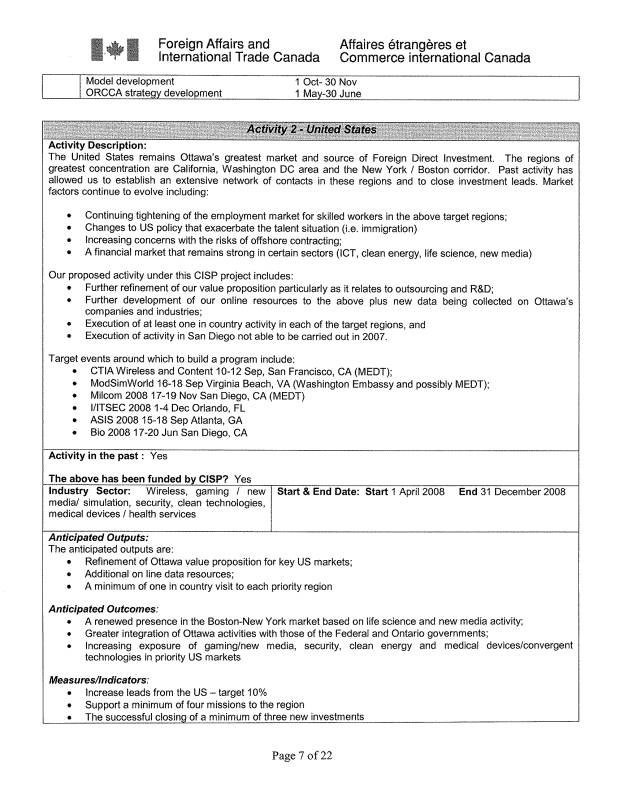
United States
The United States
remains Ottawa’s greatest market and source of Foreign Direct Investment. The regions of greatest concentration are California,
Washington DC area and the New York / Boston corridor. Past activity has allowed us to establish an
extensive network of contacts in these regions and to close investment leads.
Market factors continue to evolve including:
- Continuing tightening of the
employment market for skilled workers in the above target regions;
- Changes to US policy that exacerbate
the talent situation (i.e. immigration)
- Increasing concerns with the risks of
offshore contracting;
- A financial market that remains strong
in certain sectors (ICT, clean energy, life science, new media)
Our proposed
activity under this CISP project includes:
- Further refinement of our value
proposition particularly as it relates to outsourcing and R&D;
- Further development of our online
resources to the above plus new data being collected on Ottawa’s companies
and industries;
- Execution of at least one in country
activity in each of the target regions, and
- Execution of activity in San Diego not
able to be carried out in 2007.
Target events
around which to build a program (partners in parenthesis) include:
- CTIA Wireless and Content 10-12 Sep,
San Francisco, CA (MEDT);
- ModSimWorld 16-18 Sep Virginia Beach,
VA (Washington Embassy and possibly MEDT);
- Milcom 2008 17-19 Nov San Diego, CA
(MEDT)
- I/ITSEC 2008 1-4 Dec Orlando, FL
(MEDT)
- ASIS 2008 15-18 Sep Atlanta, GA
(Atlanta Consulate)
- Bio 2008 17-20 Jun San Diego, CA
(MEDT)
- We are also searching for an event to
anchor a Clean Energy activity in California
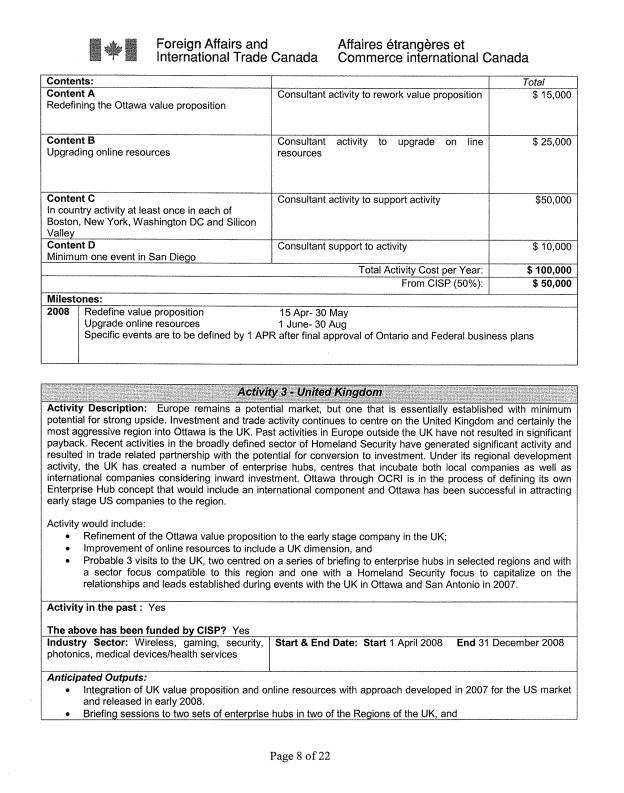
United Kingdom
Europe remains a potential market, but one that is
essentially established with minimum potential for strong upside. Investment
and trade activity continues to centre on the United Kingdom and certainly the
most aggressive region for inward investment into Ottawa is the UK. Past
activities in Europe outside the UK have not resulted in significant payback.
Recent activities in the broadly defined sector of Homeland Security have
generated significant activity and resulted in trade related partnership with
the potential for conversion to investment. Under its regional development
activity, the UK has created a number of enterprise hubs, centers that incubate
both local companies as well as international companies considering inward
investment. Ottawa through OCRI is in the process of defining its own
Enterprise Hub concept that would include an international component and Ottawa
has been successful in attracting early stage US companies to the region.
Activity would
include:
- Refinement of the Ottawa value
proposition to the early stage company in the UK;
- Improvement of online resources to
include a UK dimension, and
- Probable 3 visits to the UK, two
centered on a series of briefing to enterprise hubs in selected regions
and with a sector focus compatible to this region and one with a Homeland
Security focus to capitalize on the relationships and leads established
during events with the UK in Ottawa and San Antonio in 2007.
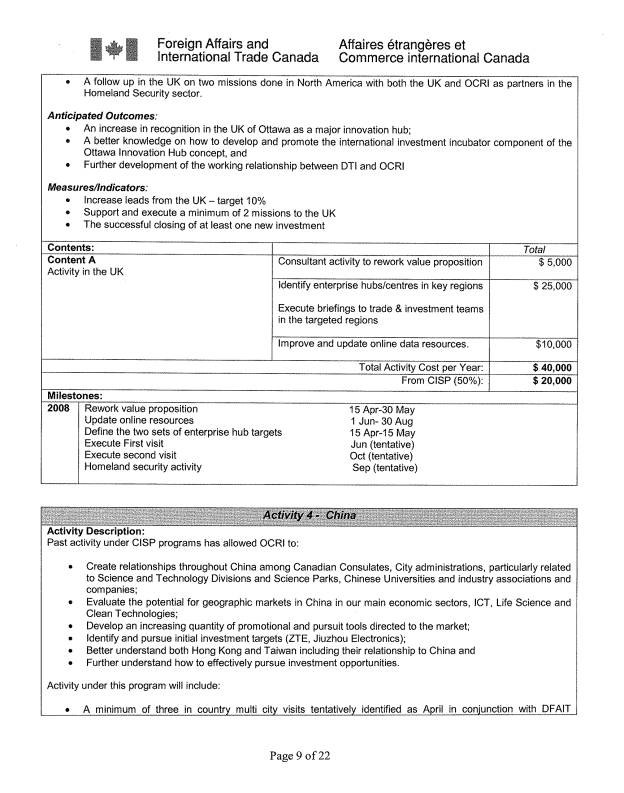
China
Background
- Over the
past year we have gained a stronger understanding of the China market
opportunities, expanded the number of active City targets, begun pursuit
of specific investments and expanded our focus to include clean energy.
- Our bank of
materials in Chinese has continued to grow. We have added to our material
on specific sectors producing mini Capability Guides from our English
material. Our website in Chinese has been overhauled.
- Intelligence has been gained through
participation in 4 regional industry events and two tours (visiting three
cities both times and one involving Taiwan). We continue to host incoming Chinese
regional missions to Ottawa on a regular basis.
- International
Trade has signed MOU’s with China on both two way trade and investment and
S&T cooperation, creating a vehicle for attracting investment and for
promoting scientific cooperation.
- China, in
its latest Party Congress, has reaffirmed its commitment to “Going Global”
and has added Clean Environment/Clean Energy to its priorities for the new
five year plan.
- We have
gained increasing knowledge on key factors driving Chinese investment.
Investment
Attraction Activity
- We will
officially sign our agreement with the ZGC Science Park in Beijing and
hopefully do the same with Chongqing and Shenzhen. We will determine our
best strategy for Shanghai.
- Target a
minimum of three receptive municipal organizations in China for potential
negotiation of an OCRI to similar organization agreement as opposed to
city to city.
- We will
continue our focus on ICT, begin active work on clean energy and initiate
activity in medical devices and convergent technologies. We have
identified multiple opportunities for events in China around which an
investment program can be built. We plan to make three trips to China, two
around planned Federal activity in ICT and Clean Energy and one to support
a planned mission in photonics by the Canadian Photonics Consortium. The
Chinese cities are Shenzhen, Chongqing, Shanghai, Beijing and Hong Kong.
One visit will include Taipei.
Our objective remains to establish Ottawa, China, i.e. Ottawa as the
preferred gateway for Chinese companies and institutions into the North
American market.
Middle East
Our present CISP
project has done research around on the Middle Eastern market. The activity in
this project will complete the initial market exploration by developing a
program around the premier ICT show in the region, GITEX, 19-23 October 2008
Dubai
India
Background
- OGM retained
an Ottawa-based firm with extensive ties in India to develop both trade
and investment opportunities in India. Two trips were made to India to
gain first hand knowledge of the market.
- Ottawa
companies are being successful in closing India business. Specific areas
of success are telecommunications infrastructure and broadband
applications.
- In the two
trips, seven qualified leads were developed. This significantly exceeded
expectations. It has been found that many Indian companies do not consider
Canada when looking to North America. The Canada value proposition does
make sense when explained.
- Data has
been developed that demonstrates that Canada can be a significant market,
with a growth potential exceeding the US. This assists in defining a value
proposition that looks to access to the US market, but demonstrates that
Canada is a significant market by itself.
- One Indian
company that has made two Ottawa investments has been identified that
serves as a strong case study for investment in the region.
- Several
Ottawa based outsourcers and software companies have developed
relationships in India
- The lead is
being made with ICT, but potential in both Clean Energy and Life Science
has been identified.
- Opportunities
to work with Indian universities on commercialization have also been
identified.
Investment
Attraction Activity
- Our activity
will centre on working the qualified leads we have to move them to
investment. They are requesting significant amounts of information and in
some we have to demonstrate our value against the US and in others against
cities in Canada with significant Indo-Canadian communities.
- Activity to
date has centred on only Tier1 cities. We will extend our activity to Tier
2 cities to increase the pipeline.
We will continue to monitor the desire of Indian universities to create
commercialization ties, particularly in the photonics sector.
Chile and Brazil
Past activity has
included:
- Two ICT missions to Chile;
- Three incoming investment inquiries
from Brazil over the last two years;
- Three Doing Business In seminars on
the region over the last two years, and
- Interest in municipal structure in Sao
Paulo from City Council and a plan visit by a Councillor in Feb 08
- ICT market studies on Chile and Brazil
have recently been completed by the Federal and Ontario governments
respectively.
The Ontario
government has in country consultants in both Sao Paulo and Santiago.
Activity under
this program will be:
- An in country visit program to Sao
Paulo and Santiago








SCHEDULE
B – OCRI (REGIONAL INNOVATION NETWORK) –
$250,000 CAPITAL REQUEST
|
OCRI (Regional Innovation Network) $
250,000 Capital Request
|
|
General Background
Information:
By way of background, Ontario’s Regional Innovation Network (RIN)
Program is based on a system of regional networks. These are
multi-stakeholder organizations established through funding from the Government
of Ontario to promote partnerships among business, academia and local
governments to promote innovation.
The merger of the Ottawa Life Science Council into OCRI formalized
OCRI as the Regional Innovation Network center for Ottawa in 2007. Under this
umbrella, OCRI, along with partners from business, academia, government,
research institutions and the community at large expanded efforts to grow
Ottawa’s knowledge based economy from life science through to Cleantech and
ICT. In 2007, OCRI was able to define programs and services to assist
companies across these sectors including the establishment of the Cleantech
Initiative, the Ottawa Medical Device (now Ottawa MedTech) Network, and
through the development of targeted service offerings to assist start up and
emerging companies access critical mentorship, market intelligence and access
to capital at critical stages.
Currently, the City of Ottawa provides an operating grant of
$250,000.00 to assist in the development and implementation of these programs
and services, including the support for 2 FTE and operating processes to
ensure program success. This $250,000 was essential to OCRI’s ability to
continue to serve the life science community while at the same time enhancing
the operational capacity to provide greater service to life sciences,
Cleantech and ICT companies within the Ottawa region and launching critical
investment and commercialization resources to meet the needs start up and
emerging companies in these knowledge based sectors.
Under this funding
program, several significant programs have been developed and/or enhanced,
over and above the base operations. These included the following:
·
Establishment
and implementation of a full service Investment and Commercialization Program
for start up and emerging companies in life science, Cleantech and ICT which
includes:
·
Access to
mentors
·
Market
Intelligence
·
Business
Advisory Services
·
Access to
Capital
·
Launch of
the OCRI Business Accelerator
·
Expansion
of the Bioproducts, Energy and Environmental Technologies Business Network
(Be2BN), now branded the Cleantech Initiative
·
Soft launch
of the Ottawa Medical Device Network (now Ottawa MedTech)
In addition, a number of significant initiatives were developed and
expanded to ensure broad reach and facilitate business activity, promote
local Ottawa companies, and celebrate Ottawa success. These include:
·
Canada’s
Top 10 Competition expanded to include Life Science, Cleantech and ICT
·
Ottawa
Venture and Technology Summit incorporated significant streams in Cleantech
and medical devices
·
Biojobs, a
recruitment portal dedicated to serving the life sciences industry in Ottawa
and Eastern Ontario was expanded and incorporated into OCRI’s job portal
·
BioNorth
expanded to include streams in clean technology and included partnerships
with RIN’s across Ontario who brought science and technology experts and
companies to Ottawa for the event.
Capital Grant Historical
Information:
- For the period January 2005 to December 31, 2008, the province
of Ontario under its Regional Innovation Network (RIN) program entered
into a contract with OLSC (now OCRI) to provide a grant not to exceed
50% of $1,400,000 over the three year period of the contract. In 2006,
the province provided OLSC \ OCRI with $250,000 in funding under this
program. The grant is based upon OCRI providing matching funding.
- On July 12, 2006, the City of Ottawa approved $250,000 from its
Capital budget to support this project
(ACS2006-PGM-ECO-0004). This
grant from the City matched funding received from Ontario in 2006. Deliverables
under this agreement are on file with the City.
- In 2007, the City of Ottawa approved an additional $250,000 from
its Capital budget to support this project. Our capital request for 2008
will be used to again provide matching funding to support the final year
of Ontario’s funding contract.
|
|
|
|
|
City Capital Request
|
Province RIN Grant
|
Total
Project
|
|
OCRI 2008 Capital Budget Request
|
$250,000
|
$260,847
|
$510,847
|
This request to the City of Ottawa will
enable OCRI to meet the growing demand for services from the Cleantech and
Ottawa MedTech Networks, growth of a therapeutics network and better linkages
to the research community, and enhance the capacity of the Investment and
Commercialization Group to build to grow start up and emerging companies in
Ottawa.
2008 OCRI City of Ottawa
Deliverables
for the Regional Innovation
Network Program
Q1
- Canada’s Top 10 Investment Forums in
Boston & New York
- Work with 6 of Canada’s Top 10 Life
Science and Cleantech companies located in Ottawa to identify and assist
in facilitating investment interest
- Work with 14 new start ups or emerging
companies through Investment and Commercialization’s Business Advisory
Services
- Facilitate 4 new mentorship contracts
to provide mentors to start up companies in partnership with IRAP
- Facilitate access of 2 new companies
into the Ontario wide Business Mentorship and Entrepreneurship Program
- Host and facilitate the launch of
Ottawa MedTech, Ottawa’s medical device cluster
- Represent Ottawa at The World Congress
on Industrial Biotechnology & Bioprocessing.
- Host a Green Buildings Showcase in
Ottawa to facilitate networking among members of the Cleantech Initiative
- Host a Clean Energy Forum in Ottawa to
bring together clean energy companies and stakeholders in partnership with
the Clean Energy Cluster
Q2
- Represent Ottawa at Bio 2008 in San
Diego including:
- Increase recognition of Ottawa as a
center for life science and Cleantech investment by US based angel
investors and Venture Capital Funds through speaking engagements at key events
associated with the conference
- Canada’s Top 10 Investment Forum in
San Francisco
- Open Canada’s Top 10 Program Call for
Applications for 2008/09
- Launch the OCRI Investment and
Commercialization Group website
- Revise the Canada’s Top 10 website
- Plan a half day workshop for angels on
investing, deal flow, and networking
- Host a series of lunch and learn
sessions for start up and emerging companies with local services providers
including banks, accounting, legal, and VC’s to facilitate knowledge
transfer and networking
- Transition one company out of the OCRI
Business Accelerator upon successful financing
- Transition one new company into the
OCRI Business Accelerator
- Facilitate Business Advisory Services
and access to Ontario wide programs with 15 new start up companies in
Ottawa
- Promote Investment and
Commercialization Group services at BioFinance 2008
- Host a Cleantech Breakfast for local
companies, researchers and stakeholders
- Begin planning BioNorth 2008
- Host a Hospital Research Day
- Cleantech Research Showcase – May 28th
Lansdowne Park (NRC, NRCan, Carleton U, Ottawa U, Algonquin, U of Guelph
Kemptville Campus)
- Spring Ottawa Cleantech Report
(newsletter)
- ‘Cleantech Connections’ online
directory and collaboration tools
- Cleantech Breakfast – Focus on water
Q3
- Promote BioNorth
- Host a Co-Investment Summit in
partnership with the National Angel Organization and local angels
- Facilitate Business Advisory Services
and access to Ontario wide programs with 15 new start up companies in
Ottawa
- Organize and host the Ottawa Life
Sciences Achievement Awards
- Facilitate a series of networking
events for Ottawa MedTech
- Outreach to surrounding counties
- Cleantech Breakfast
- Fall Ottawa Cleantech Report
- Initiatives to attract qualified
talent to the region for our clean technology companies
- ‘How Green is Green?’ lecture
Q4
- Attend the National Angel Organization
Summit in Halifax representing Ottawa
- Announce Canada’s Top 10 Winners
- Host the Ottawa Venture and Technology
Summit featuring a showcase of local Ottawa companies and the Canada’s Top
10 winners
- Facilitate Business Advisory Services
and access to Ontario wide programs with 15 new start up companies in
Ottawa
- Deliver BioNorth 2008
- Host Canada’s Top 10 Investment
Bootcamp
- Attend the North American Venture
Summit as a delegate
- Cleantech Breakfast
- Capping event for 2008
- Winter Ottawa Cleantech Report
SCHEDULE C – OCRI (ONTARIO RESEARCH COMMERCIALIZATION
PROJECT)
- $100,000 CAPITAL REQUEST
|
Ontario Research
Commercialization Project (ORCP) $100,000 Capital Request
|
|
As part of a
request to provide proposals to the Provincial Governments (MRI’s) Ontario
research Commercialization Project (ORCP), OCRI has developed an Ottawa
response entitled the Regional Innovation Development Program (RIDP.) This is
a collaborative initiative to improve “receptor capacity” – to help build the
existing technology-based Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and start-ups,
to accelerate technology and knowledge transfer, and to create more viable
and successful businesses, in order to develop a stronger economic base for
growth.
Four distinct projects are included within the Ottawa RIDP (details
can be found below):
- Project #1 – Market/Competitive
Intelligence Project
- Project #2 – Business Opportunity
Networks
- Project #3 – Entrepreneur Development
- Project #4 – Convergence Exploration
This is the
second year of funding as part of a 3 year provincial program to fund
commercialization activities in Ottawa. The province is providing
direct funding of $1,800,000 over
three years.
The City approved $100,000 of capital funding
in 2006 and in 2007 to support
activity in year one and year two. This money has been used to support the
partnership component of the project, given that the Province’s contribution
cannot exceed 50% of total cash and in kind expenses. Therefore the current capital request of $100,000 will be used to further
support the partnership component of the project. The cash expenditure budget
for the project is summarized below.
|
|
20/20
Plan Policy #
10, 11, 15, 20, 22
|
The following sections describe each of the projects, as they were
initially proposed to MRI, within the ORCP to be completed and how they fit
into the Ottawa innovation framework.
In addition, other related programs are briefly shown how they also link
into the framework.
Framework Element:
Information Services
The Market/Competitive Intelligence program originally
focused on the life sciences and Cleantech industries. After a market
assessment and demand from other sectors in Ottawa, the decision was made to
provide this service offering to companies across life science, Cleantech and
ICT. Instead of an electronic portal for access to web-based queries, and to
manage subscription agreements with data management partners, a Manager of
Market Intelligence was hired to facilitate the enquiry process and provide
additional business analysis and support to companies as required. Additionally,
an in-house library has been established at OCRI providing outside members with
access to previously downloaded reports which are sectorally focused.
Currently, OCRI has subscription agreements with
Under the initial contract, access to technical
intelligence was be provided by two dedicated and trained staff with
proprietary access (valued at $250K/yr.) to the vast electronic libraries of
NRC-CISTI (one of the largest of its kind in the world, with about $7.5 million
of new acquisitions annually).
The program was to initially focus on the creation of
a multi-tiered portal for the content (i.e. secured, members-only and
administrative partners-only web access) with intelligence resources made
available to our partners and members.
NRC-CISTI capacity allows for access to resources within their vast
library system on a contract basis. It was determined with our NRC partner that
the contract be amended to better serve companies by providing them with
customized searches provided by in-house NRC-CISTI staff as opposed to
recruiting, training and retaining NRC –CISTI employees on site. Also,
NRC-CISTI employee recruitment process can take upwards of one year to complete
and there was an urgent need to find a solution suitable to local businesses.
Changes to operations have not changed accessibility
by partners and members under the terms of the ORCP program. The users of the
system are primarily two-fold. First
are the Business Development Officers who are assisting with the development of
business and marketing plans for the research spin-out opportunities. Second are those who are directly involved
in the research activities. That is,
the “members” and “partners” are the universities, colleges and hospitals
(primarily in the life science sectors) that OCRI engages with in research as
part of their other Ontario funding programs, including RIN activities. This also extends to companies across life
science and clean tech where there is a need to better understand the market
and positioning prior to entering the market. This “intelligence” information
is a critical missing element that will help determine where best to focus an
application of research or prototype as it moves from the lab into potential
market and product development.
The requests made by the users of the system can
easily be tracked and the value of the information assessed by the end user
(research or business oriented). This
feedback can be then used to help focus on those specific services that provide
more value and help tailor the process to those needs.
Implementation:
·
This program
maintains focus on life science industries and has been expanded to include
clean technologies, including clean energy, and ICT. The program is managed by
OCRI Investment and Commercialization.
·
NRC-CISTI
will work with OCRI’s Investment and Commercialization Group and specifically
its Manager, Market Intelligence, to deliver Competitive Technical Intelligence
(CTI) services on a customized and request by request basis. Technical intelligence materials that CISTI
can provide continue to include patent search results, technical journals and
reports, conference proceedings, and similar materials. Under this partnership, NRC-CISTI support
includes a reduced fee for service for access to technical information
specialists and in-house business analysts on an as needed basis.
·
Business
Insights will reduce the subscription rate for unlimited access subscription to
Business Insights reports across life science, Cleantech and ICT. Deloitte and
PricewaterhouseCoopers will also provide unlimited access to their proprietary
market and competitive intelligence research reports, having an approximate
value of $20K/yr each ($10K staff “in-kind” and $10K materials).
·
Business
Mentorship and Entrepreneurship Program (BMEP), administered by MaRS, is part
of an Ontario wide program to assist early stage companies. Through BMEP, OCRI
will utilize more than $100K in reports for companies from data management
companies like Frost and Sullivan, Gartners, Thomson Financial, and others.
Framework Element:
Business Development
Successful commercialization requires interaction
among all of the individuals, associations, and potential research
opportunities (within universities, colleges and government labs) that support
R&D, innovation and commercialization within the region, as well as with
partnerships outside the region. It has
been said that exploring for new opportunities, finding alliances, and creating
collaboration in this space is a “body contact sport,” meaning that these
interactions usually require face-to-face dealings to be most effective. Often SMEs are reluctant to explore third
party IP opportunities or cannot spend their time, money, or resources to
explore and identify such alliances.
The SMEs need a team of individuals who are always on the “look out” for
them. As such, these individuals
provide a common point of “go to” for the SME that they can use to help search
for solutions, opportunities and create alliances. In essence, this project is like building a tech-transfer
capability that represents the SME community in their continual search for
opportunities.
Briefly, the objective of the Business Opportunity
Networks Program is to provide the SME community with a small team of competent
“opportunity seekers” (Business Development Officers) with technical, business,
and community understanding as well as direct experience in working with the
cultural and motivational differences that exist between the SMEs, research
labs, and the business community at large.
The team would bring an expanded network through their interface with
representatives from the university/college tech-transfer offices and other
provincial programs such as OCE and other ORCP funded programs. With one of their primary focuses being the
regular interaction with these external partnership and opportunity sources,
the formation of a strengthened opportunities and best practices network would
be established further supporting the commercialization of technologies or the
strengthening of existing companies. As
part of this initiative, the Ottawa team members would work with their counter
parts in other regions (e.g. Waterloo and Toronto) to share potential
prospects, best practices, and establish industry-academic linkages between
regions to build a greater pan-provincial understanding and create a more
integrated service package.
As Business Development Officers, these experienced
business individuals will first contact the SME senior management and begin
building the business case. As such,
individuals will be “field based” and spend the bulk of their time visiting
potential clients in their own environment.
Armed with this information, they will be able to populate a database to
share amongst other regions. Then,
during the course of their regular business interactions and networking with
tech transfer offices and other organizations at investor meetings, innovation
workshops, etc., they will work on making valuable connections that can further
engage the SME. These development
specialists will also help marshal resources from other RIDP programs (such as
using mentor networks, application of market readiness funds, suggesting
training courses, etc.) towards helping solve identified needs.
In summary, a list of duties to be performed by a
Business Development Officer would be to:
Maintain a portfolio of SMEs for which they work on
behalf to look for research, business and market opportunities;
·
Collect and
distribute relevant data regarding potential opportunities (through common
databases, project reports, progress summaries, meetings, etc.);
·
Provide a
conduit and linkage to tech-transfer offices in academic and government labs;
·
Provide
access and support of RIDP and other commercialization programs (such as OCE,
IRAP, etc.) to be delivered to the SME; and,
·
Network, not
only amongst themselves to share ideas and best practice implementations, but
also to engage in other regional and provincial technology networks and
programs.
As the foundation of the Business Opportunity
Networks, the Business Development Officers are providing that critical
“people” connectivity for the SME to the research, business, funding, etc.
networks. They fill the critical roll
of providing the skills, time, resources, and cultural understanding to the
world “outside” – a gap the SMEs experience as they focus on their day-to-day
business to the exclusion of looking outwards to be better receptors of
research.
Each regional partner in the RIDP (Ottawa, Waterloo,
and Toronto) has different implementation needs and would hire Business
Development Officers with differing talent and skills reflecting their
priorities among the above duties to be filled. This approach provides the greatest flexibility in program delivery
and in achieving success based on the unique characteristics of each region.
Implementation:
·
Each Business
Development Officer will leverage other services within the city and region
such as connecting SME’s to the Entrepreneurship Centre or the CI/MI resources.
·
This program
complements the existing OCRI Cluster Support Program. With new Business Development Officers in
place, the Clusters (each who have their own network of technology-based SMEs)
would now have direct linkages to new research and commercialization
opportunities.
·
Provide
additional resources to aid the Ottawa Capital Network focus on new Life
Sciences deals and opportunities.
·
Includes the
hiring of two full-time Business Development Officers (primarily ICT), with
complementary business, marketing and technology skills and include additional
partnering activities.
·
Working with
similar individuals in other organizations (such as the OCE and NRC’s IRAP
business development officers), a larger network of technology and funding
support can be engaged.
·
It is
expected that the Business Development Officers in each of the regions will
actively exchange ideas and information, in addition to having regular
quarterly group meetings and workshops.
In this way, efficient processes can be developed and cross provincial
opportunities created (e.g. industry working with a university in a different
region).
·
NOTE: Business Development Officers for the life
sciences industry are already in place and funded through OLSC RIN funding.
Framework Element:
Entrepreneur & Talent Development; Network Interaction
An entrepreneur is an agent of change – he or she
recognizes an opportunity and acts upon it.
It is through the development of the entrepreneur as a person that
long-term sustainable economical growth of small companies can be
achieved. A successful region is one
that develops a supply of highly skilled entrepreneurs who are capable of
building successful companies in sufficient numbers to transform the economy of
that region. It has been recognized
that, with the proper skills, entrepreneurs can indeed be “made”, and need not
be “born”.
There is no doubt that there are many things for
entrepreneurs to learn as an SME grows in its early stages, not only internal
corporate activities but also engaging with the community and through knowledge
transfer. This project is aimed at
helping them focus on their needs and developing essential skills. Individual business mentoring is one
important way to do this, but there are significant advantages in group
activities and shared experiences. Not
only do these activities expose entrepreneurs to new opportunities, but also
they enable the entrepreneurs to build their own networks. The Entrepreneur Development program is
directly aimed at filling the skills gap experienced by the entrepreneur and
opening them up to networks that expand their interaction with researchers (and
thus aiding to bridge the culture gap) and business opportunities.
There are several forums that provide development
opportunities and knowledge-transfer for entrepreneurs:
·
“Boot-camps”
at which individuals (often with only technology experience) learn the
fundamentals of running a technology-based SME.
·
Business
training and courses offered at local universities and colleges.
·
Venture Fairs
at which SMEs present their business proposition to investors.
·
Conferences
that provide a showcase of successes as well as providing the opportunity to
create ongoing strategy for developing and growing SMEs within a region.
·
Educational
initiatives that create a culture of entrepreneurship within students, and
provide them with the necessary skills to both start and build their own
businesses.
·
Workshops and
networking events that bring together those in the community engaged in
innovation and commercialization directly with the SMEs.
·
A host of
existing formal and informal networks and clusters within regions (e.g.
wireless network, software network, photonics network, Bioproducts, Energy and
Environmental Technologies Business Network, Convergent Medical and Assistive
Technology (CMAT) network, etc.) are critical to the exchange of information,
the transfer of knowledge, and aiding the convergence of technologies.
Implementation:
·
Led and
managed by Ottawa RIDP Program Manager with support from their team at the
Entrepreneurship Centre.
·
OCRI has a
semi-formal program of workshops, boot camps, seminars, and a VC fair that it
would build upon to form a more regular and consistent development program; the
OLSC is active through their programs such as Canada’s Top 10 life Sciences
Company program, the BioEntrepreneurs series and Professional Development
series as well as specific series directed for the Business Opportunity Network
Constituents. Under the merger, the two
efforts will be efficiently coordinated as applicable.
·
Also, the new
OCRI will align with local university schools of business and consultants that
supply training courses for entrepreneurs and students to support access to
those programs
·
Engage expertise
and support from OCE, the Ottawa Angel Alliance and other Angel groups, local
venture capital firms, the Ottawa cluster groups (e.g. Wireless, Software,
Photonics, Semiconductor, Security, Bioproducts, Energy and Environmental
Technologies, and Medical and Assistive Technologies).
·
OCRI’s
entrepreneur training workshops (E2) are planned for January, May
and September of each year. The VC fair
is scheduled for the fall of each year.
·
Planning
sessions are being scheduled for April and October each year. At these sessions, the RIDP staff from
Ottawa will prepare summaries of the previous activities, adjust program
delivery and plan for the next 6 months.
It is anticipated that these meetings will involve other RIDP regions
including Toronto and Waterloo so that experiences and best practices can be
shared.
Framework Element:
Business Development
In the early stages, the RIDP concept was developed
with the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector as its focus –
the major technology strength of the Ottawa region. The three major regions (Ottawa, Waterloo and Toronto) along the
Ontario technology corridor cover about 85% of the province’s ICT industrial
base and leading academic institutions.
Also, ICT are pervasive and enabling technologies that accelerate the
development of many other sectors as they also continue to grow.
This enabling approach is not unique to the ICT
industry, but applies to the major industry sectors (manufacturing, life sciences,
aerospace, etc.). OCRI Life Sciences
has also been developing a similar innovation framework for the life sciences
industry. The merging of OCRI and OLSC
has provided an excellent opportunity for a common innovation framework (as
described above). At the same time, it
is recognized that time-to-market and approach-to-market issues are different
for each sector within the respective industries (i.e. software,
semiconductors, drug discovery, bio medical devices and bio products are all
unique), the RIDP implementation can be used for any of them and in support of
cross-sector initiatives.
The OCRI/OLSC merger initiates a look at ICT and life
sciences industry innovation and commercialization opportunities (e.g.
bioinformatics). This Convergence Exploration
program is set to also explore linkages with other sectors, including
automotive, aerospace, energy, manufacturing, financial, etc. Canada faces a major innovation and
commercialization gap by not having efforts focused on opportunities that link
together sectors. This value-add
approach that focuses on these types of projects will help to uniquely position
and link several economic sectors important to Ontario.
Including a Convergence Exploration program is
critical in support of SMEs in order to take advantage of:
·
The growing
trend in R&D “convergence” that integrates often diverse technologies.
·
Engaging
clusters to create a critical mass exploration of technology and
commercialization opportunities that might not otherwise exist.
·
Providing
complementary skills in the development of new, and often complex, technology
and market opportunities.
·
Connecting
the right people from the right organizations regardless of sector or geography
·
Driving to
the requirement to be an active player in the rapidly developing global
economy.
This program is a link into other Ontario innovation
and commercialization programs within MRI (that include the ORCP, OCE, MaRS,
Ontario Research Funds, and the Regional Innovation Networks (RINs)) that
address a variety of technology and industry sectors.
Implementation:
·
The Ottawa
RIDP (OCRI) is also linked to the Waterloo (Communitech) and Toronto (ISCM and
MaRS) equivalents. As part of the
provincial-wide initiative, coordination with their programs will be
implemented.
·
Because of
the importance of the initiative, the President of each of the organizations
will be the individual lead, with support from their senior staff and the RIDP
Business Development Officers.
·
Regular
meetings between them will be established to share ideas and look for
multi-sector opportunities.
SCHEDULE D – OCRI GLOBAL MARKETING (CLUSTER SUPPORT) –
$70,000 CAPITAL REQUEST
|
OCRI Global Marketing
(Cluster Support) $70,000
Capital Request
|
|
General Background
Information:
- Within the Ottawa 20/20 plan, the region was committed to a
cluster-based economic development policy
- OCRI developed a cluster support model that would support the
growth of clusters within the region while minimizing the demand for new
funds, making maximum utilization of existing resources in the region
and freeing private sector resources to concentrate on strategic
initiatives.
- In 2006, a two year pilot project was launched to prove the
validity of the model to end in March 2008.
- The pilot project was successful in creating a logistic support
system that is now supporting 8 clusters through a set of productivity
tools within the Global Marketing section of OCRI.
- The Business Development function within OGM is now fully integrated
into the clusters
- The clusters have defined a series of strategic initiatives that
will assist in the strengthening and growth of the Ottawa economy. These
include:
- Software: High School Pilot Technology Centre Project
- Security: Federal Industrial Benefits Capture
Initiative
- Contact Centres: Industry recognition campaign
- Semiconductor: Joint Targeted Marketing
Initiative
- Funds to support these initiatives are available from both
government programs and industry. This requires coordination of the
partners, preparation of funding documentation and partnership
agreements and monitoring and assistance during execution.
High School Pilot Technology Centre Project
Background
·
Registration
in Science and Technology programs in Ottawa post secondary institutions
reached record lows in school year 2007-2008
·
High School
students demonstrate an adversity to enter the requisite courses for entry to
post secondary Science and Technology courses.
·
Ottawa
companies are encountering difficulty in recruiting young talent
·
Secondary
schools have difficulty in maintaining technology infrastructure and
appropriately trained teachers
·
OCRI, in
conjunction with the Software Cluster and the Earl Of March High School ran a
highly successful series of events in 2007 that were well received by
students
·
The Ontario
Centres of Excellence are highly supportive of the initiative and the
Ministry of Colleges Training and Universities have expressed their
willingness to partner
·
Carleton
University, the University of Ottawa and Algonquin College are participating
in project definition
·
Corporations
that are participating in project definition are IBM, Cisco, RIM, Dell and
Macadamian Technologies
Objectives
·
Establish a
pilot to demonstrate how a private sector supported regional technology centre
could be used to deliver approved high school curricula in technology on a
sustainable basis
·
Establish
preferential entry to post secondary institutions for graduates of technology
courses in high school
·
Expand
existing coop and summer work programs in high school to integrate with the
technology curriculum
·
Transfer the program to the Ministry of
Education for long term funding
Work program
·
Identify an
existing private sector technology centre that could be made available to the
project for one day a week
·
With a
selected group of high schools, implement credit programs for the school year
2008-2009
·
Implement a
work experience program
Federal Industrial Benefits Capture Initiative
Background
Over the past
five years, the Canadian SME sector has been lobbying the Federal government
to open up its procurement system to facilitate business capture by SME’s.
For the most part, this has been a frustrating experience. A potentially much
more rewarding opportunity exists that involves not a SME to government
transaction, but a business to business transaction.
The Canadian
Government, and more particularly the Department of National Defence, is
embarking on a series of major capital programs. In the majority of these
programs, the equipment cannot be supplied from the Canadian industrial base
and must be supplied by a foreign supplier. To maximize the benefit of these
programs to Canadian industry, the procurement contracts contain obligations
on the prime contractor to identify and place contracts with Canadian
industry. These industrial benefits can either be direct, ie goods and
services produced in Canada related to the prime contract, or indirect
benefits which are goods and services procured by the prime contractor and
designated subcontractors not related to the capital program.
Although Canada
had a number of capital programs throughout the last decades of the past
century, this level of activity has not occurred over the past several years.
The result is a general lack of awareness amongst Canadian industry of the
Industrial Offset opportunity. Furthermore, increasing emphasis is being
placed by the government on indirect benefits and knowledge based industries.
The Ottawa industrial base is uniquely positioned to take advantage of this
opportunity.
Challenges to
successful revenue capture by Canadian industry include:
·
Insufficient
knowledge of the Canadian industrial offset program and its operation;
·
Limited
knowledge of the specific programs and their offset obligations:
·
The
difficulty of identifying the various operating units of primes and their
subs and the contacts within those units;
·
Limited
knowledge on how to execute an effective business development function to
capture contracts, and
·
The lack of
any effective mechanism to link companies with offset obligations to
companies looking for opportunities.
Objectives
- Build awareness among Ottawa’s
exporting SME’s of the opportunities within the Federal Industrial
Offset program and provide education on techniques to successfully
capture business
- Build a database of existing
industrial offset obligations
- Build a database of appropriate
contacts among prior contractors and their first and second tier
suppliers
- Execute pilot visits to identified
high probability contractors
- Capture revenue for Ottawa firms
Work plan
The project
would have four components:
1.
Awareness
Building: A series of
two hour briefings would be given to industry, either by cluster or in
general forums to make industry aware of the opportunities. This would be
followed by a series of more interactive one day seminars on effective
business development strategies. The briefings would be delivered by industry
experts and contain a talk by at least one successful SME. The seminars will
be led by an industry expert and again include a successful SME and a Prime
contractor.
2.
Research: A database will be developed of the
present programs and their obligations. This will include the Prime
contractor and the contact for offsets. For each contract this data will be
extended to subcontractors for which offsets can be claimed. This research
will be progressively extended to the operating locations or specific
divisions of all contractors being tracked.
3.
Contractor
Visit Program: OCRI
Global Marketing (OGM), working with industry partners, will begin the
identification of contractors most likely to yield offset opportunities. A
series of site visits or visits to Ottawa will then be coordinated for small
group visits between Ottawa SME’s and the identified contractor. This
activity will extend beyond the principal operating location of the
contractor working on the contract into other divisions and operating
locations. This activity will be executed in partnership with individual
clusters, prime contractors, International Trade’s in country staff and
experts in the Ottawa region. This program will be executed through OGM’s
Business Development staff as a pilot in 2008 and then fully integrated into
its 2009 Business Plan.
4.
Matching
Service: Using its
existing productivity management tools, OGM will build the capacity to link
members of the Ottawa Knowledge Based Industry to offset opportunities.
Contact Centre Industry Recognition Program
Background
·
Ottawa has
seen a significant growth in its contact centre business and they are now
major employers in the region
·
Ottawa’s
industry is strongest in the financial sector and technical support
·
The jobs
are well paying and provide excellent career opportunities
·
The
industry suffers from a major image problem, as being low paying and dead end
·
The
industry has increasing recruiting challenges, both from poor image amongst
potential employee base and among influencers to young people
·
The
industry has established a task force to address the situation
·
A survey
has been done to obtain base data on the industry
·
Under a
separate project, a long term strategy for growth is being developed
Objectives
- Create awareness amongst the general
public of the positive nature of the industry, its growth potential and
its career benefits
- Create awareness amongst the pool of
potential employees of the nature of the industry in Ottawa and its
potential as a career
- Create awareness amongst influencers
of high school students of the industry and its potential as a career.
- Demonstrate to potential investors
from outside the region that Ottawa supports the industry and is
strengthening the regional infrastructure to support the industry
Work plan
- Finalize the campaign parameters and
industry funding, Apr-Jun 08
- Create the campaign, July-Aug 08
- Execute Phase 1 of the campaign,
Sep-Dec 08
- Evaluate the results of Phase 1,
Jan-Mar 09
Semiconductor Partnering Initiative
Background
- OGM recently worked with the Federal
government on a highly successful Wireless mission to the WiMax Forum in
Taiwan. Four of the eight companies chosen for participation were Ottawa
based.
- Ottawa is known for its niche
technologies, unfortunately by their nature they must be integrated into
higher order systems. In that process, the value of our technologies is
often overlooked
- Throughout the world, auctions are
occurring for new telecommunications spectrum, creating a considerable
demand for WiMax products
- SiGe identified their difficulty in
creating senior management recognition of their solutions during the
Taiwan mission. Too often decisions, on their product are made by lower
level component designers in the company or its suppliers without
reference to benefits at higher levels of integration. Taiwan is the
centre for the higher order products.
- SiGe is willing to lead an industry
group to address this challenge through a specific focus on the WiMax
opportunity and are preparing a White Paper to circulate amongst other
Ottawa companies in a similar situation
- The challenge is creating the
marketing mass to present several aspects of a solution to a customer rather
than the narrow focus presented by a single company and its products
- If this initiative proves
successful, it will serve as a template for similar coordinated industry
marketing efforts
Objectives
- Establish a tight group of companies
to develop a cooperative marketing and sales approach to companies in
Taiwan.
- Increase the success rate of these
companies in the market
- Establish the case for cooperative
marketing to meet the challenges of the position of our companies in the
global supply chain
Work Plan
·
Completion
of the White Paper by 1 Apr
·
Definition
of the group of companies and development of a cooperative strategy by 1 June
08
·
Pilot
implementation of the activity through to Dec 08.
·
Evaluation
of the results Jan-Mar 09.
|
Funding
We are seeking 70K
in funding for the period 1 Apr 08- 31 Mar 09. This funding would be to provide
one full time junior program management individual and one half time clerical
individual to support the administration and execution of the above projects.
Expected leverage
of direct project costs and in kind support is:
- High School Pilot Technology Centre:
$120K
- Federal Industrial Benefits Capture
Initiative: $150K
- Contact Centre Industry Recognition
Project: $75 K
- Semiconductor Partnering Initiative:
$80K
It is therefore
expected that the City investment of $70K would leverage $425K in other short
term project funding.
|
OCRI 2008 Capital Budget Request Details
|
City Capital Request
|
Other Support
|
Total
Project
|
|
Consulting Fees
|
70,000
|
|
70,000
|
|
Other Direct /
In Kind project costs
|
-
|
425,000
|
425,000
|
|
|
$70,000
|
$425,000
|
$495,000
|
2008 Cluster Capital Ask
High
School Pilot Technology Project
Costs
Facility
Company mentoring
Sponsor related
tests
|
In-kind
(18,500)
(15,000)
(5,000)
|
0
|
Program
Administrator
|
|
$22,500
|
Teachers
(OCRI tech coaches)
|
$200-$300
per day x 2 teachers
|
$12,000
|
Teacher
Training- train 3
|
$200 per
day x 3 teachers x 10 days
|
$6,000
|
Curriculum
Development (one time)
|
In-kind
(10,000)
|
0
|
Consumables
|
|
$1,000
|
Transportation
of students
|
$150 x 20
day
|
$3,000
|
Certification
Tests
Based on
30 students @150 per certification test
|
3 tests x
$150
|
$13,500
|
Approx
Total per Semester Cash
|
|
$57,500
|
For two
semesters, $115,000 direct $77,000
in kind
Revenue
Cash
- Ontario Centres of Excellence
$60K
- Large Co’s $30K
- SME’s $5K
- Ontario Ministry of Colleges and Universities $20K
Federal
Industrial Benefits Capture Initiative
Costs
Awareness Building
- Content development
$10,000 (in kind)
- Two hour seminars $10,000 (in kind)
- 1 Day seminars $40,000
($10,000 in kind, $30,000 industry recovery)
Research
Contractor Visits
- Contractor selection and logistics set up $10,000 in kind
- In country assistance (DFAIT)
$15,000 Federal
- Company Travel costs
$40,000 in kind
Company Matching
- OGM system modifications $10 K Federal
- Execution of service $ 5K in-kind
Contact
Centre Industry Recognition Program
Campaign Strategy Development $10k
in kind
Material Development $15K $10K in
kind $5K industry contribution
Printing, reproduction $20K industry
contribution
Commercial Placement costs $25K industry contribution
In school activity $5K in kind
Targeted
Marketing Initiative
Campaign development, in country meetings,
in country logistics $80 K Federal
Company definition and coordination $20K in
kind
Marketing strategy development $30K
in kind
Travel $50K
in kind






















